Projected climate variability of internal waves in the Andaman Sea
Published:
Abstract:
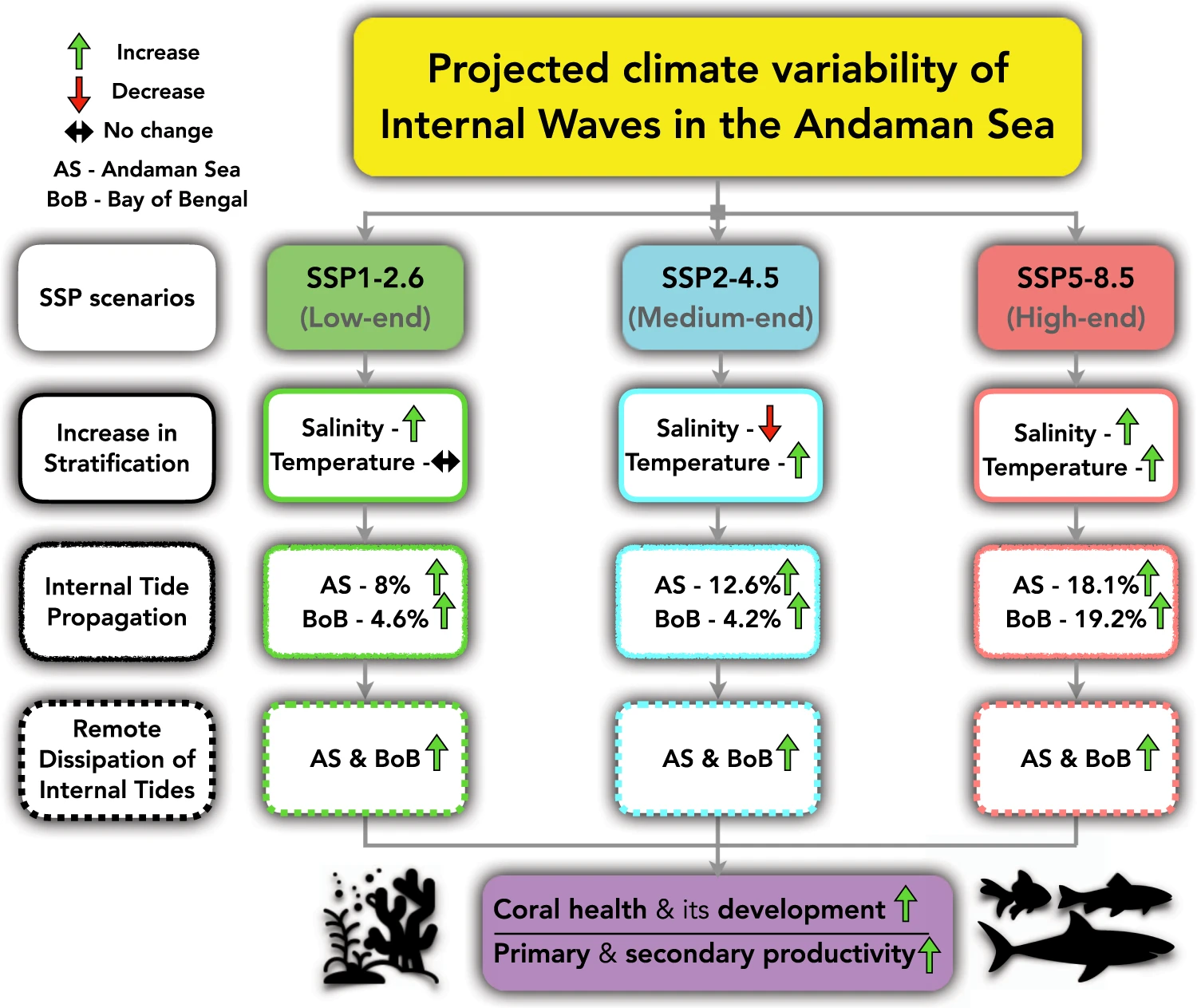
The Andaman Sea, in the northeast Indian Ocean, is renowned for large-amplitude internal waves. Here, we use a global climate model (CanESM5) to investigate the long-term variability of internal waves in the Andaman Sea under a range of shared socioeconomic pathway (SSP) scenarios. SSPs are future societal development pathways related to emissions and land use scenarios. We project that mean values of depth-averaged stratification will increase by approximately 6% (SSP1-2.6), 7% (SSP2-4.5), and 12% (SSP5-8.5) between 1871-1900 and 2081-2100. Simulating changes in internal tides between the present (2015-2024) and the end-century (2091-2100), we find that the increase in stratification will enhance internal tide generation by approximately 4 to 8%. We project that the propagation of internal tides into the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal will increase by 8 to 18% and 4 to 19%, respectively, under different SSP scenarios. Such changes in internal tides under global warming will have implications for primary production and ecosystem health not only in the Andaman Sea but also in the Bay of Bengal.
Summary